- Slovenia
-
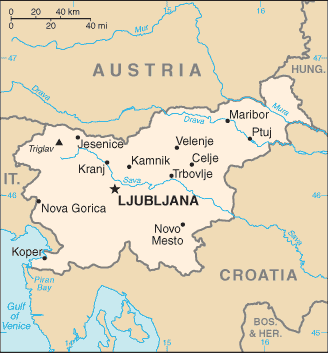 Introduction ::SloveniaBackground:The Slovene lands were part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire until the latter's dissolution at the end of World War I. In 1918, the Slovenes joined the Serbs and Croats in forming a new multinational state, which was named Yugoslavia in 1929. After World War II, Slovenia became a republic of the renewed Yugoslavia, which though communist, distanced itself from Moscow's rule. Dissatisfied with the exercise of power by the majority Serbs, the Slovenes succeeded in establishing their independence in 1991 after a short 10-day war. Historical ties to Western Europe, a strong economy, and a stable democracy have assisted in Slovenia's transformation to a modern state. Slovenia acceded to both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004; it joined the eurozone in 2007.Geography ::SloveniaLocation:south Central Europe, Julian Alps between Austria and CroatiaGeographic coordinates:46 07 N, 14 49 EArea:total: 20,273 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 155land: 20,151 sq kmwater: 122 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than New JerseyLand boundaries:total: 1,086 kmborder countries: Austria 330 km, Croatia 455 km, Hungary 102 km, Italy 199 kmCoastline:46.6 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmClimate:Mediterranean climate on the coast, continental climate with mild to hot summers and cold winters in the plateaus and valleys to the eastTerrain:a short coastal strip on the Adriatic, an alpine mountain region adjacent to Italy and Austria, mixed mountains and valleys with numerous rivers to the eastElevation extremes:lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 mhighest point: Triglav 2,864 mNatural resources:lignite coal, lead, zinc, building stone, hydropower, forestsLand use:arable land: 8.31%permanent crops: 1.33%other: 90.36% (2011)Irrigated land:76.04 sq km (2010)Total renewable water resources:31.87 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 0.94 cu km/yr (18%/82%/0%)per capita: 462.9 cu m/yr (2009)Natural hazards:flooding; earthquakesEnvironment - current issues:Sava River polluted with domestic and industrial waste; pollution of coastal waters with heavy metals and toxic chemicals; forest damage near Koper from air pollution (originating at metallurgical and chemical plants) and resulting acid rainEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:despite its small size, this eastern Alpine country controls some of Europe's major transit routesPeople and Society ::SloveniaNationality:noun: Slovene(s)adjective: SlovenianEthnic groups:Slovene 83.1%, Serb 2%, Croat 1.8%, Bosniak 1.1%, other or unspecified 12% (2002 census)Languages:Slovenian (official) 91.1%, Serbo-Croatian 4.5%, other or unspecified 4.4%, Italian (official, only in municipalities where Italian national communities reside), Hungarian (official, only in municipalities where Hungarian national communities reside) (2002 census)Religions:Catholic 57.8%, Muslim 2.4%, Orthodox 2.3%, other Christian 0.9%, unaffiliated 3.5%, other or unspecified 23%, none 10.1% (2002 census)Population:1,992,690 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Age structure:0-14 years: 13.4% (male 137,756/female 129,420)15-24 years: 10.3% (male 105,182/female 100,255)25-54 years: 44.2% (male 444,274/female 435,702)55-64 years: 14.7% (male 144,230/female 147,774)65 years and over: 17.5% (male 138,953/female 209,144) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 46 %youth dependency ratio: 20.9 %elderly dependency ratio: 25.2 %potential support ratio: 4 (2013)Median age:total: 43.1 yearsmale: 41.4 yearsfemale: 44.9 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.21% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 215Birth rate:8.66 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 215Death rate:11.12 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Net migration rate:0.38 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 70Urbanization:urban population: 50% of total population (2010)rate of urbanization: 0.2% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:LJUBLJANA (capital) 260,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.66 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:28.7 (2010 est.)Maternal mortality rate:12 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 151Infant mortality rate:total: 4.08 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 198male: 4.61 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 3.52 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 77.66 yearscountry comparison to the world: 61male: 74.02 yearsfemale: 81.53 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.32 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 211Contraceptive prevalence rate:78.9%note: percent of women aged 15-44 (1994/95)Health expenditures:9.4% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 38Physicians density:2.47 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:4.6 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 99% of populationtotal: 99% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 1% of populationtotal: 1% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 100% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:less than 0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 131HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:fewer than 1,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 145HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 141Obesity - adult prevalence rate:28.6% (2008)country comparison to the world: 33Education expenditures:5.7% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 49Literacy:definition: NAtotal population: 99.7%male: 99.7%female: 99.7% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 17 yearsmale: 16 yearsfemale: 18 years (2011)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 15.7%country comparison to the world: 82male: 15%female: 16.8% (2011)Government ::SloveniaCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Sloveniaconventional short form: Slovenialocal long form: Republika Slovenijalocal short form: Slovenijaformer: People's Republic of Slovenia, Socialist Republic of SloveniaGovernment type:parliamentary republicCapital:name: Ljubljanageographic coordinates: 46 03 N, 14 31 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in OctoberAdministrative divisions:200 municipalities (obcine, singular - obcina) and 11 urban municipalities (mestne obcine, singular - mestna obcina)municipalities: Ajdovscina, Apace, Beltinci, Benedikt, Bistrica ob Sotli, Bled, Bloke, Bohinj, Borovnica, Bovec, Braslovce, Brda, Brezice, Brezovica, Cankova, Cerklje na Gorenjskem, Cerknica, Cerkno, Cerkvenjak, Cirkulane, Crensovci, Crna na Koroskem, Crnomelj, Destrnik, Divaca, Dobje, Dobrepolje, Dobrna, Dobrova-Polhov Gradec, Dobrovnik/Dobronak, Dolenjske Toplice, Dol pri Ljubljani, Domzale, Dornava, Dravograd, Duplek, Gorenja Vas-Poljane, Gorisnica, Gorje, Gornja Radgona, Gornji Grad, Gornji Petrovci, Grad, Grosuplje, Hajdina, Hoce-Slivnica, Hodos, Horjul, Hrastnik, Hrpelje-Kozina, Idrija, Ig, Ilirska Bistrica, Ivancna Gorica, Izola/Isola, Jesenice, Jezersko, Jursinci, Kamnik, Kanal, Kidricevo, Kobarid, Kobilje, Kocevje, Komen, Komenda, Kosanjevica na Krki, Kostel, Kozje, Kranjska Gora, Krizevci, Krsko, Kungota, Kuzma, Lasko, Lenart, Lendava/Lendva, Litija, Ljubno, Ljutomer, Log-Dragomer, Logatec, Loska Dolina, Loski Potok, Lovrenc na Pohorju, Luce, Lukovica, Majsperk, Makole, Markovci, Medvode, Menges, Metlika, Mezica, Miklavz na Dravskem Polju, Miren-Kostanjevica, Mirna, Mirna Pec, Mislinja, Mokronog-Trebelno, Moravce, Moravske Toplice, Mozirje, Muta, Naklo, Nazarje, Odranci, Oplotnica, Ormoz, Osilnica, Pesnica, Piran/Pirano, Pivka, Podcetrtek, Podlehnik, Podvelka, Poljcane, Polzela, Postojna, Prebold, Preddvor, Prevalje, Puconci, Race-Fram, Radece, Radenci, Radlje ob Dravi, Radovljica, Ravne na Koroskem, Razkrizje, Recica ob Savinji, Rence-Vogrsko, Ribnica, Ribnica na Pohorju, Rogaska Slatina, Rogasovci, Rogatec, Ruse, Selnica ob Dravi, Semic, Sevnica, Sezana, Slovenska Bistrica, Slovenske Konjice, Sodrazica, Solcava, Sredisce ob Dravi, Starse, Straza, Sveta Ana, Sveta Trojica v Slovenskih Goricah, Sveti Andraz v Slovenskih Goricah, Sveti Jurij ob Scavnici, Sveti Jurij v Slovenskih Goricah, Sveti Tomaz, Salovci, Sempeter-Vrtojba, Sencur, Sentilj, Sentjernej, Sentjur, Sentrupert, Skocjan, Skofja Loka, Skofljica, Smarje pri Jelsah, Smarjeske Toplice, Smartno ob Paki, Smartno prurban municipalities: Celje, Koper-Capodistria, Kranj, Ljubljana, Maribor, Murska Sobota, Nova Gorica, Novo Mesto, Ptuj, Slovenj Gradec, VelenjeIndependence:25 June 1991 (from Yugoslavia)National holiday:Independence Day/Statehood Day, 25 June (1991)Constitution:adopted 23 December 1991; amended 14 July 1997 and 25 July 2000Legal system:civil law systemInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age, 16 if employed; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Borut PAHOR (since 22 December 2012)head of government: Prime Minister Alenka BRATUSEK (since 20 March 2013)cabinet: Council of Ministers nominated by the prime minister and elected by the National Assembly(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 11 November and a runoff on 2 December 2012 (next presidential election to be held in 2017); following National Assembly elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of a majority coalition usually nominated to become prime minister by the president and elected by the National Assemblyelection results: Borut PAHOR elected president; percent of vote - Borut PAHOR 67.4%, Danilo TURK 32.6%; on February 27, 2013 a no-confidence vote in Parliament resulted in Alenka BRATUSEK becoming prime minister designate; BRATUSEK became prime minister (Slovenia's first female prime minister) on 20 March 2013 after her cabinet was approvedLegislative branch:bicameral Parliament consists of a National Council or Drzavni Svet (40 seats; members indirectly elected by an electoral college to serve five-year terms; note - this is primarily an advisory body with limited legislative powers; it may propose laws, ask to review any National Assembly decision, and call national referenda) and the National Assembly or Drzavni Zbor (90 seats; 88 members are elected on a proportional basis and 2 are elected by the Italian and Hungarian minorities through a majoritarian, preferential system; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)elections: National Assembly - last held on 4 December 2011 (next to be held in 2015)election results: percent of vote by party - PS 28.6%, SDS 26.2%, SD 10.5%, LGV 8.4%, DeSUS 7%, SLS 6.9%, NSi 4.8%, other 7.6%; seats by party - PS 28, SDS 26, SD 10, LGV 8, DeSUS 6, SLS 6, NSi 4, Hungarian minority 1, Italian minority 1Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the court president and 37 judges organized into 7 departments - civil, criminal, commercial, labor and social security, administrative, registry, and international cooperation); Constitutional Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and 7 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court president and vice president appointed by the National Assembly upon the proposal of the Minister of Justice based on the opinions of the Judicial Council, an 11-member independent body elected by the National Assembly from proposals submitted by the president, attorneys, law universities, and sitting judges; other Supreme Court judges elected by the National Assembly from candidates proposed by the Judicial Council; Supreme Court judge term NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the National Assembly from nominations by the president of the republic; Constitutional Court president selected from among their own for a 3-year term; other judges elected for single 9-year termssubordinate courts: county, district, regional, and high courts; specialized labor-related and social courts; Court of Audit; Administrative CourtPolitical parties and leaders:Civic List or DL [Gregor VIRANT] (formerly LGV)Democratic Party of Pensioners of Slovenia or DeSUS [Karl ERJAVEC]New Slovenia or NSi [Ljudmila NOVAK]Positive Slovenia or PS [Alenka BRATUSEK (interim)]Slovene People's Party or SLS [Radovan ZERJAV]Slovenian Democratic Party or SDS [Janez JANSA]Social Democrats or SD [Igor LUKSIC] (formerly ZLSD)Political pressure groups and leaders:Slovenian Roma Association [Jozek Horvat MUC]; various trade and public sector employee unionsother: Catholic ChurchInternational organization participation:Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA (cooperating state), EU, FAO, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Roman KIRNchancery: 2410 California Street N.W., Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 386-6601FAX: [1] (202) 386-6633consulate(s) general: Cleveland, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Joseph A. MUSSOMELIembassy: Presernova 31, 1000 Ljubljanamailing address: American Embassy Ljubljana, US Department of State, 7140 Ljubljana Place, Washington, DC 20521-7140telephone: [386] (1) 200-5500FAX: [386] (1) 200-5555Flag description:three equal horizontal bands of white (top), blue, and red, derive from the medieval coat of arms of the Duchy of Carniola; the Slovenian seal (a shield with the image of Triglav, Slovenia's highest peak, in white against a blue background at the center; beneath it are two wavy blue lines depicting seas and rivers, and above it are three six-pointed stars arranged in an inverted triangle, which are taken from the coat of arms of the Counts of Celje, the great Slovene dynastic house of the late 14th and early 15th centuries) appears in the upper hoist side of the flag centered on the white and blue bandsNational symbol(s):Mount TriglavNational anthem:name: ""Zdravljica"" (A Toast)lyrics/music: France PRESEREN/Stanko PREMRLnote: adopted 1989; the anthem was originally written in 1848; the full poem, whose seventh verse is used as the anthem, speaks of pan-Slavic nationalismEconomy ::SloveniaEconomy - overview:Slovenia became the first 2004 European Union entrant to adopt the euro (on 1 January 2007) and has experienced one of the most stable political and economic transitions in Central and Southeastern Europe. With the highest per capita GDP in Central Europe, Slovenia has excellent infrastructure, a well-educated work force, and a strategic location between the Balkans and Western Europe. Privatization has lagged since 2002, and the economy has one of the highest levels of state control in the EU. Structural reforms to improve the business environment have allowed for somewhat greater foreign participation in Slovenia's economy and helped to lower unemployment. In March 2004, Slovenia became the first transition country to graduate from borrower status to donor partner at the World Bank. In 2007, Slovenia was invited to begin the process for joining the OECD; it became a member in 2012. Despite its economic success, foreign direct investment (FDI) in Slovenia has lagged behind the region average, and taxes remain relatively high. Furthermore, the labor market is often seen as inflexible, and legacy industries are losing sales to more competitive firms in China, India, and elsewhere. In 2009, the global recession caused the economy to contract - through falling exports and industrial production - by 8%, and unemployment to rise. Although growth resumed in 2010, it dipped into negative territory in 2012 and the unemployment rate continued to rise, approaching 12% in 2012.GDP (purchasing power parity):$58.91 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 91$60.32 billion (2011 est.)$59.96 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$45.62 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:-2.3% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2100.6% (2011 est.)1.2% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$28,700 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 54$29,400 (2011 est.)$29,300 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:18.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8519.1% of GDP (2011 est.)20.2% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 58.3%government consumption: 20.6%investment in fixed capital: 17.4%investment in inventories: -0.3%exports of goods and services: 75%imports of goods and services: -71%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 2.7%industry: 27.7%services: 69.6% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:potatoes, hops, wheat, sugar beets, corn, grapes; cattle, sheep, poultryIndustries:ferrous metallurgy and aluminum products, lead and zinc smelting; electronics (including military electronics), trucks, automobiles, electric power equipment, wood products, textiles, chemicals, machine toolsIndustrial production growth rate:0.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 129Labor force:920,200 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 2.2%industry: 35%services: 62.8% (2009)Unemployment rate:12% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 12611.8% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:13.6% (2011)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 3.9%highest 10%: 19.8% (2011)Distribution of family income - Gini index:23.8 (2011)country comparison to the world: 13523.8 (2004)Budget:revenues: $20.06 billionexpenditures: $21.86 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:44% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-3.9% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 138Public debt:53.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5641.9% of GDP (2011 est.)note: defined by the EU's Maastricht Treaty as consolidated general government gross debt at nominal value, outstanding at the end of the year in the following categories of government liabilities: currency and deposits, securities other than shares excluding financial derivatives, and loans; general government sector comprises the subsectors: central government, state government, local government, and social security fundsFiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.6% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 701.8% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:1.5% (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 1231.75% (31 December 2011)note: this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro areaCommercial bank prime lending rate:5.73% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1445.82% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$16.03 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 66$16.12 billion (31 December 2010 est.)note: see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own bordersStock of broad money:$26.52 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 79$25.62 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$49.34 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 65$48.54 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$6.326 billion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 74$9.428 billion (31 December 2010)$11.77 billion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:$297.6 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 49$2.505 million (2011 est.)Exports:$27.58 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 67$29.59 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:manufactured goods, machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, foodExports - partners:Germany 20%, Italy 12%, Austria 7.9%, Croatia 6.2%, France 4.8%, Russia 4.6% (2012)Imports:$28.01 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 67$31.05 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, chemicals, fuels and lubricants, foodImports - partners:Italy 16.3%, Germany 16.2%, Austria 10.4%, Croatia 4.8%, Hungary 4% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$951.9 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 138$991.3 million (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$53.88 billion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 59$52.07 billion (31 December 2011)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$17.36 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 71$16.71 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$9.755 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 55$9.405 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:euros (EUR) per US dollar -0.7778 (2012 est.)0.7185 (2011 est.)0.755 (2010 est.)0.7198 (2009 est.)0.6827 (2008 est.)Energy ::SloveniaElectricity - production:15.61 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 79Electricity - consumption:11.6 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 84Electricity - exports:10.14 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Electricity - imports:8.014 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Electricity - installed generating capacity:3.4 million kW (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Electricity - from fossil fuels:42.2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 167Electricity - from nuclear fuels:21.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:34.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - from other renewable sources:1.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Crude oil - production:5 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 181Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Crude oil - proved reserves:NA bbl (1 January 2012 est.)Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Refined petroleum products - consumption:52,930 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 96Refined petroleum products - exports:11,500 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Refined petroleum products - imports:60,270 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Natural gas - production:7 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Natural gas - consumption:1.06 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 88Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 177Natural gas - imports:1.053 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 58Natural gas - proved reserves:NA cu m (1 January 2012 est.)Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:17.42 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Communications ::SloveniaTelephones - main lines in use:872,800 (2011)country comparison to the world: 84Telephones - mobile cellular:2.168 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 138Telephone system:general assessment: well-developed telecommunications infrastructuredomestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity roughly 150 telephones per 100 personsinternational: country code - 386 (2011)Broadcast media:public TV broadcaster, Radiotelevizija Slovenija (RTV), operates a system of national and regional TV stations; 35 domestic commercial TV stations operating nationally, regionally, and locally; about 60% of households are connected to multi-channel cable TV; public radio broadcaster operates 3 national and 4 regional stations; more than 75 regional and local commercial and non-commercial radio stations (2007)Internet country code:.siInternet hosts:415,581 (2012)country comparison to the world: 54Internet users:1.298 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 92Transportation ::SloveniaAirports:16 (2013)country comparison to the world: 143Airports - with paved runways:total: 7over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 3under 914 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 91,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 3under 914 m:5 (2013)Pipelines:gas 844 km; oil 5 km (2013)Railways:total: 1,228 kmcountry comparison to the world: 84standard gauge: 1,228 km 1.435-m gauge (503 km electrified) (2007)Roadways:total: 38,925 kmcountry comparison to the world: 93paved: 38,925 km (includes 658 km of expressways) (2008)Waterways:(there is some transport on the Drava River) (2012)Merchant marine:registered in other countries: 24 (Cyprus 5, Liberia 7, Malta 4, Marshall Islands 6, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 1, Slovakia 1) (2010)country comparison to the world: 90Ports and terminals:KoperMilitary ::SloveniaMilitary branches:Slovenian Armed Forces (Slovenska Vojska, SV): Forces Command (with ground units, naval element, air and air defense brigade); Administration for Civil Protection and Disaster Relief (ACPDR) (2013)Military service age and obligation:18-25 years of age for voluntary military service; conscription abolished in 2003 (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 477,592females age 16-49: 464,301 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 392,075females age 16-49: 380,077 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 9,818female: 9,395 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.7% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Transnational Issues ::SloveniaDisputes - international:since the breakup of Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, Croatia and Slovenia have each claimed sovereignty over Pirin Bay and four villages, and Slovenia has objected to Croatia's claim of an exclusive economic zone in the Adriatic Sea; in 2009, however Croatia and Slovenia signed a binding international arbitration agreement to define their disputed land and maritime borders, which led to Slovenia lifting its objections to Croatia joining the EU; Slovenia continues to impose a hard border Schengen regime with Croatia, which joined the EU in 2013 but has not yet fulfilled Schengen requirements; as a member state that forms part of the EU's external border, Slovenia has implemented the strict Schengen border rules to curb illegal migration and commerce through southeastern Europe while encouraging close cross-border ties with CroatiaIllicit drugs:minor transit point for cocaine and Southwest Asian heroin bound for Western Europe, and for precursor chemicals"
Introduction ::SloveniaBackground:The Slovene lands were part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire until the latter's dissolution at the end of World War I. In 1918, the Slovenes joined the Serbs and Croats in forming a new multinational state, which was named Yugoslavia in 1929. After World War II, Slovenia became a republic of the renewed Yugoslavia, which though communist, distanced itself from Moscow's rule. Dissatisfied with the exercise of power by the majority Serbs, the Slovenes succeeded in establishing their independence in 1991 after a short 10-day war. Historical ties to Western Europe, a strong economy, and a stable democracy have assisted in Slovenia's transformation to a modern state. Slovenia acceded to both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004; it joined the eurozone in 2007.Geography ::SloveniaLocation:south Central Europe, Julian Alps between Austria and CroatiaGeographic coordinates:46 07 N, 14 49 EArea:total: 20,273 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 155land: 20,151 sq kmwater: 122 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than New JerseyLand boundaries:total: 1,086 kmborder countries: Austria 330 km, Croatia 455 km, Hungary 102 km, Italy 199 kmCoastline:46.6 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmClimate:Mediterranean climate on the coast, continental climate with mild to hot summers and cold winters in the plateaus and valleys to the eastTerrain:a short coastal strip on the Adriatic, an alpine mountain region adjacent to Italy and Austria, mixed mountains and valleys with numerous rivers to the eastElevation extremes:lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 mhighest point: Triglav 2,864 mNatural resources:lignite coal, lead, zinc, building stone, hydropower, forestsLand use:arable land: 8.31%permanent crops: 1.33%other: 90.36% (2011)Irrigated land:76.04 sq km (2010)Total renewable water resources:31.87 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 0.94 cu km/yr (18%/82%/0%)per capita: 462.9 cu m/yr (2009)Natural hazards:flooding; earthquakesEnvironment - current issues:Sava River polluted with domestic and industrial waste; pollution of coastal waters with heavy metals and toxic chemicals; forest damage near Koper from air pollution (originating at metallurgical and chemical plants) and resulting acid rainEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:despite its small size, this eastern Alpine country controls some of Europe's major transit routesPeople and Society ::SloveniaNationality:noun: Slovene(s)adjective: SlovenianEthnic groups:Slovene 83.1%, Serb 2%, Croat 1.8%, Bosniak 1.1%, other or unspecified 12% (2002 census)Languages:Slovenian (official) 91.1%, Serbo-Croatian 4.5%, other or unspecified 4.4%, Italian (official, only in municipalities where Italian national communities reside), Hungarian (official, only in municipalities where Hungarian national communities reside) (2002 census)Religions:Catholic 57.8%, Muslim 2.4%, Orthodox 2.3%, other Christian 0.9%, unaffiliated 3.5%, other or unspecified 23%, none 10.1% (2002 census)Population:1,992,690 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Age structure:0-14 years: 13.4% (male 137,756/female 129,420)15-24 years: 10.3% (male 105,182/female 100,255)25-54 years: 44.2% (male 444,274/female 435,702)55-64 years: 14.7% (male 144,230/female 147,774)65 years and over: 17.5% (male 138,953/female 209,144) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 46 %youth dependency ratio: 20.9 %elderly dependency ratio: 25.2 %potential support ratio: 4 (2013)Median age:total: 43.1 yearsmale: 41.4 yearsfemale: 44.9 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:-0.21% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 215Birth rate:8.66 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 215Death rate:11.12 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Net migration rate:0.38 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 70Urbanization:urban population: 50% of total population (2010)rate of urbanization: 0.2% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:LJUBLJANA (capital) 260,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.66 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:28.7 (2010 est.)Maternal mortality rate:12 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 151Infant mortality rate:total: 4.08 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 198male: 4.61 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 3.52 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 77.66 yearscountry comparison to the world: 61male: 74.02 yearsfemale: 81.53 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:1.32 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 211Contraceptive prevalence rate:78.9%note: percent of women aged 15-44 (1994/95)Health expenditures:9.4% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 38Physicians density:2.47 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:4.6 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 99% of populationtotal: 99% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 1% of populationtotal: 1% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 100% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:less than 0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 131HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:fewer than 1,000 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 145HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 141Obesity - adult prevalence rate:28.6% (2008)country comparison to the world: 33Education expenditures:5.7% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 49Literacy:definition: NAtotal population: 99.7%male: 99.7%female: 99.7% (2011 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 17 yearsmale: 16 yearsfemale: 18 years (2011)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 15.7%country comparison to the world: 82male: 15%female: 16.8% (2011)Government ::SloveniaCountry name:conventional long form: Republic of Sloveniaconventional short form: Slovenialocal long form: Republika Slovenijalocal short form: Slovenijaformer: People's Republic of Slovenia, Socialist Republic of SloveniaGovernment type:parliamentary republicCapital:name: Ljubljanageographic coordinates: 46 03 N, 14 31 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in OctoberAdministrative divisions:200 municipalities (obcine, singular - obcina) and 11 urban municipalities (mestne obcine, singular - mestna obcina)municipalities: Ajdovscina, Apace, Beltinci, Benedikt, Bistrica ob Sotli, Bled, Bloke, Bohinj, Borovnica, Bovec, Braslovce, Brda, Brezice, Brezovica, Cankova, Cerklje na Gorenjskem, Cerknica, Cerkno, Cerkvenjak, Cirkulane, Crensovci, Crna na Koroskem, Crnomelj, Destrnik, Divaca, Dobje, Dobrepolje, Dobrna, Dobrova-Polhov Gradec, Dobrovnik/Dobronak, Dolenjske Toplice, Dol pri Ljubljani, Domzale, Dornava, Dravograd, Duplek, Gorenja Vas-Poljane, Gorisnica, Gorje, Gornja Radgona, Gornji Grad, Gornji Petrovci, Grad, Grosuplje, Hajdina, Hoce-Slivnica, Hodos, Horjul, Hrastnik, Hrpelje-Kozina, Idrija, Ig, Ilirska Bistrica, Ivancna Gorica, Izola/Isola, Jesenice, Jezersko, Jursinci, Kamnik, Kanal, Kidricevo, Kobarid, Kobilje, Kocevje, Komen, Komenda, Kosanjevica na Krki, Kostel, Kozje, Kranjska Gora, Krizevci, Krsko, Kungota, Kuzma, Lasko, Lenart, Lendava/Lendva, Litija, Ljubno, Ljutomer, Log-Dragomer, Logatec, Loska Dolina, Loski Potok, Lovrenc na Pohorju, Luce, Lukovica, Majsperk, Makole, Markovci, Medvode, Menges, Metlika, Mezica, Miklavz na Dravskem Polju, Miren-Kostanjevica, Mirna, Mirna Pec, Mislinja, Mokronog-Trebelno, Moravce, Moravske Toplice, Mozirje, Muta, Naklo, Nazarje, Odranci, Oplotnica, Ormoz, Osilnica, Pesnica, Piran/Pirano, Pivka, Podcetrtek, Podlehnik, Podvelka, Poljcane, Polzela, Postojna, Prebold, Preddvor, Prevalje, Puconci, Race-Fram, Radece, Radenci, Radlje ob Dravi, Radovljica, Ravne na Koroskem, Razkrizje, Recica ob Savinji, Rence-Vogrsko, Ribnica, Ribnica na Pohorju, Rogaska Slatina, Rogasovci, Rogatec, Ruse, Selnica ob Dravi, Semic, Sevnica, Sezana, Slovenska Bistrica, Slovenske Konjice, Sodrazica, Solcava, Sredisce ob Dravi, Starse, Straza, Sveta Ana, Sveta Trojica v Slovenskih Goricah, Sveti Andraz v Slovenskih Goricah, Sveti Jurij ob Scavnici, Sveti Jurij v Slovenskih Goricah, Sveti Tomaz, Salovci, Sempeter-Vrtojba, Sencur, Sentilj, Sentjernej, Sentjur, Sentrupert, Skocjan, Skofja Loka, Skofljica, Smarje pri Jelsah, Smarjeske Toplice, Smartno ob Paki, Smartno prurban municipalities: Celje, Koper-Capodistria, Kranj, Ljubljana, Maribor, Murska Sobota, Nova Gorica, Novo Mesto, Ptuj, Slovenj Gradec, VelenjeIndependence:25 June 1991 (from Yugoslavia)National holiday:Independence Day/Statehood Day, 25 June (1991)Constitution:adopted 23 December 1991; amended 14 July 1997 and 25 July 2000Legal system:civil law systemInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:18 years of age, 16 if employed; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Borut PAHOR (since 22 December 2012)head of government: Prime Minister Alenka BRATUSEK (since 20 March 2013)cabinet: Council of Ministers nominated by the prime minister and elected by the National Assembly(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 11 November and a runoff on 2 December 2012 (next presidential election to be held in 2017); following National Assembly elections, the leader of the majority party or the leader of a majority coalition usually nominated to become prime minister by the president and elected by the National Assemblyelection results: Borut PAHOR elected president; percent of vote - Borut PAHOR 67.4%, Danilo TURK 32.6%; on February 27, 2013 a no-confidence vote in Parliament resulted in Alenka BRATUSEK becoming prime minister designate; BRATUSEK became prime minister (Slovenia's first female prime minister) on 20 March 2013 after her cabinet was approvedLegislative branch:bicameral Parliament consists of a National Council or Drzavni Svet (40 seats; members indirectly elected by an electoral college to serve five-year terms; note - this is primarily an advisory body with limited legislative powers; it may propose laws, ask to review any National Assembly decision, and call national referenda) and the National Assembly or Drzavni Zbor (90 seats; 88 members are elected on a proportional basis and 2 are elected by the Italian and Hungarian minorities through a majoritarian, preferential system; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)elections: National Assembly - last held on 4 December 2011 (next to be held in 2015)election results: percent of vote by party - PS 28.6%, SDS 26.2%, SD 10.5%, LGV 8.4%, DeSUS 7%, SLS 6.9%, NSi 4.8%, other 7.6%; seats by party - PS 28, SDS 26, SD 10, LGV 8, DeSUS 6, SLS 6, NSi 4, Hungarian minority 1, Italian minority 1Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the court president and 37 judges organized into 7 departments - civil, criminal, commercial, labor and social security, administrative, registry, and international cooperation); Constitutional Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and 7 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court president and vice president appointed by the National Assembly upon the proposal of the Minister of Justice based on the opinions of the Judicial Council, an 11-member independent body elected by the National Assembly from proposals submitted by the president, attorneys, law universities, and sitting judges; other Supreme Court judges elected by the National Assembly from candidates proposed by the Judicial Council; Supreme Court judge term NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the National Assembly from nominations by the president of the republic; Constitutional Court president selected from among their own for a 3-year term; other judges elected for single 9-year termssubordinate courts: county, district, regional, and high courts; specialized labor-related and social courts; Court of Audit; Administrative CourtPolitical parties and leaders:Civic List or DL [Gregor VIRANT] (formerly LGV)Democratic Party of Pensioners of Slovenia or DeSUS [Karl ERJAVEC]New Slovenia or NSi [Ljudmila NOVAK]Positive Slovenia or PS [Alenka BRATUSEK (interim)]Slovene People's Party or SLS [Radovan ZERJAV]Slovenian Democratic Party or SDS [Janez JANSA]Social Democrats or SD [Igor LUKSIC] (formerly ZLSD)Political pressure groups and leaders:Slovenian Roma Association [Jozek Horvat MUC]; various trade and public sector employee unionsother: Catholic ChurchInternational organization participation:Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA (cooperating state), EU, FAO, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Roman KIRNchancery: 2410 California Street N.W., Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 386-6601FAX: [1] (202) 386-6633consulate(s) general: Cleveland, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Joseph A. MUSSOMELIembassy: Presernova 31, 1000 Ljubljanamailing address: American Embassy Ljubljana, US Department of State, 7140 Ljubljana Place, Washington, DC 20521-7140telephone: [386] (1) 200-5500FAX: [386] (1) 200-5555Flag description:three equal horizontal bands of white (top), blue, and red, derive from the medieval coat of arms of the Duchy of Carniola; the Slovenian seal (a shield with the image of Triglav, Slovenia's highest peak, in white against a blue background at the center; beneath it are two wavy blue lines depicting seas and rivers, and above it are three six-pointed stars arranged in an inverted triangle, which are taken from the coat of arms of the Counts of Celje, the great Slovene dynastic house of the late 14th and early 15th centuries) appears in the upper hoist side of the flag centered on the white and blue bandsNational symbol(s):Mount TriglavNational anthem:name: ""Zdravljica"" (A Toast)lyrics/music: France PRESEREN/Stanko PREMRLnote: adopted 1989; the anthem was originally written in 1848; the full poem, whose seventh verse is used as the anthem, speaks of pan-Slavic nationalismEconomy ::SloveniaEconomy - overview:Slovenia became the first 2004 European Union entrant to adopt the euro (on 1 January 2007) and has experienced one of the most stable political and economic transitions in Central and Southeastern Europe. With the highest per capita GDP in Central Europe, Slovenia has excellent infrastructure, a well-educated work force, and a strategic location between the Balkans and Western Europe. Privatization has lagged since 2002, and the economy has one of the highest levels of state control in the EU. Structural reforms to improve the business environment have allowed for somewhat greater foreign participation in Slovenia's economy and helped to lower unemployment. In March 2004, Slovenia became the first transition country to graduate from borrower status to donor partner at the World Bank. In 2007, Slovenia was invited to begin the process for joining the OECD; it became a member in 2012. Despite its economic success, foreign direct investment (FDI) in Slovenia has lagged behind the region average, and taxes remain relatively high. Furthermore, the labor market is often seen as inflexible, and legacy industries are losing sales to more competitive firms in China, India, and elsewhere. In 2009, the global recession caused the economy to contract - through falling exports and industrial production - by 8%, and unemployment to rise. Although growth resumed in 2010, it dipped into negative territory in 2012 and the unemployment rate continued to rise, approaching 12% in 2012.GDP (purchasing power parity):$58.91 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 91$60.32 billion (2011 est.)$59.96 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$45.62 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:-2.3% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2100.6% (2011 est.)1.2% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$28,700 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 54$29,400 (2011 est.)$29,300 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:18.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8519.1% of GDP (2011 est.)20.2% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 58.3%government consumption: 20.6%investment in fixed capital: 17.4%investment in inventories: -0.3%exports of goods and services: 75%imports of goods and services: -71%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 2.7%industry: 27.7%services: 69.6% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:potatoes, hops, wheat, sugar beets, corn, grapes; cattle, sheep, poultryIndustries:ferrous metallurgy and aluminum products, lead and zinc smelting; electronics (including military electronics), trucks, automobiles, electric power equipment, wood products, textiles, chemicals, machine toolsIndustrial production growth rate:0.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 129Labor force:920,200 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 2.2%industry: 35%services: 62.8% (2009)Unemployment rate:12% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 12611.8% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:13.6% (2011)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 3.9%highest 10%: 19.8% (2011)Distribution of family income - Gini index:23.8 (2011)country comparison to the world: 13523.8 (2004)Budget:revenues: $20.06 billionexpenditures: $21.86 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:44% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-3.9% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 138Public debt:53.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5641.9% of GDP (2011 est.)note: defined by the EU's Maastricht Treaty as consolidated general government gross debt at nominal value, outstanding at the end of the year in the following categories of government liabilities: currency and deposits, securities other than shares excluding financial derivatives, and loans; general government sector comprises the subsectors: central government, state government, local government, and social security fundsFiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.6% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 701.8% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:1.5% (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 1231.75% (31 December 2011)note: this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro areaCommercial bank prime lending rate:5.73% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1445.82% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$16.03 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 66$16.12 billion (31 December 2010 est.)note: see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own bordersStock of broad money:$26.52 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 79$25.62 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$49.34 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 65$48.54 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$6.326 billion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 74$9.428 billion (31 December 2010)$11.77 billion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:$297.6 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 49$2.505 million (2011 est.)Exports:$27.58 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 67$29.59 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:manufactured goods, machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, foodExports - partners:Germany 20%, Italy 12%, Austria 7.9%, Croatia 6.2%, France 4.8%, Russia 4.6% (2012)Imports:$28.01 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 67$31.05 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, chemicals, fuels and lubricants, foodImports - partners:Italy 16.3%, Germany 16.2%, Austria 10.4%, Croatia 4.8%, Hungary 4% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$951.9 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 138$991.3 million (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$53.88 billion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 59$52.07 billion (31 December 2011)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$17.36 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 71$16.71 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$9.755 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 55$9.405 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Exchange rates:euros (EUR) per US dollar -0.7778 (2012 est.)0.7185 (2011 est.)0.755 (2010 est.)0.7198 (2009 est.)0.6827 (2008 est.)Energy ::SloveniaElectricity - production:15.61 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 79Electricity - consumption:11.6 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 84Electricity - exports:10.14 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Electricity - imports:8.014 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Electricity - installed generating capacity:3.4 million kW (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Electricity - from fossil fuels:42.2% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 167Electricity - from nuclear fuels:21.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:34.5% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Electricity - from other renewable sources:1.8% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Crude oil - production:5 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 181Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Crude oil - proved reserves:NA bbl (1 January 2012 est.)Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Refined petroleum products - consumption:52,930 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 96Refined petroleum products - exports:11,500 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Refined petroleum products - imports:60,270 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Natural gas - production:7 million cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Natural gas - consumption:1.06 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 88Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 177Natural gas - imports:1.053 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 58Natural gas - proved reserves:NA cu m (1 January 2012 est.)Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:17.42 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Communications ::SloveniaTelephones - main lines in use:872,800 (2011)country comparison to the world: 84Telephones - mobile cellular:2.168 million (2011)country comparison to the world: 138Telephone system:general assessment: well-developed telecommunications infrastructuredomestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity roughly 150 telephones per 100 personsinternational: country code - 386 (2011)Broadcast media:public TV broadcaster, Radiotelevizija Slovenija (RTV), operates a system of national and regional TV stations; 35 domestic commercial TV stations operating nationally, regionally, and locally; about 60% of households are connected to multi-channel cable TV; public radio broadcaster operates 3 national and 4 regional stations; more than 75 regional and local commercial and non-commercial radio stations (2007)Internet country code:.siInternet hosts:415,581 (2012)country comparison to the world: 54Internet users:1.298 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 92Transportation ::SloveniaAirports:16 (2013)country comparison to the world: 143Airports - with paved runways:total: 7over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 3under 914 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 91,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 3under 914 m:5 (2013)Pipelines:gas 844 km; oil 5 km (2013)Railways:total: 1,228 kmcountry comparison to the world: 84standard gauge: 1,228 km 1.435-m gauge (503 km electrified) (2007)Roadways:total: 38,925 kmcountry comparison to the world: 93paved: 38,925 km (includes 658 km of expressways) (2008)Waterways:(there is some transport on the Drava River) (2012)Merchant marine:registered in other countries: 24 (Cyprus 5, Liberia 7, Malta 4, Marshall Islands 6, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 1, Slovakia 1) (2010)country comparison to the world: 90Ports and terminals:KoperMilitary ::SloveniaMilitary branches:Slovenian Armed Forces (Slovenska Vojska, SV): Forces Command (with ground units, naval element, air and air defense brigade); Administration for Civil Protection and Disaster Relief (ACPDR) (2013)Military service age and obligation:18-25 years of age for voluntary military service; conscription abolished in 2003 (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 477,592females age 16-49: 464,301 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 392,075females age 16-49: 380,077 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 9,818female: 9,395 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:1.7% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Transnational Issues ::SloveniaDisputes - international:since the breakup of Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, Croatia and Slovenia have each claimed sovereignty over Pirin Bay and four villages, and Slovenia has objected to Croatia's claim of an exclusive economic zone in the Adriatic Sea; in 2009, however Croatia and Slovenia signed a binding international arbitration agreement to define their disputed land and maritime borders, which led to Slovenia lifting its objections to Croatia joining the EU; Slovenia continues to impose a hard border Schengen regime with Croatia, which joined the EU in 2013 but has not yet fulfilled Schengen requirements; as a member state that forms part of the EU's external border, Slovenia has implemented the strict Schengen border rules to curb illegal migration and commerce through southeastern Europe while encouraging close cross-border ties with CroatiaIllicit drugs:minor transit point for cocaine and Southwest Asian heroin bound for Western Europe, and for precursor chemicals"
The World Factbook. 2014.
